Code
knitr::opts_chunk$set(echo = TRUE, message = FALSE, warning = FALSE)May 24, 2023
---
title: "Untitled"
format:
html:
toc: true
toc-location: left
code-fold: true
theme: yeti
execute:
message: false
warning: false
------
title: "Untitled"
format:
html_document:
toc: true
toc-location: left
code_folding: true
theme: yeti
---(example writing) To determine the relationships between numerical variables in our dataset, we calculated Pearsons r and visually represented correlation using a correlation plot.
(example) To determine how species and physiological characteristics predict biomass, we fit multiple linear models.
We visually assess normality and homoskedasticity of residuals using diagnostic plots for the full model:
We also tested for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test (null hypothesis: variable of interest (i.e. the residuals) are normally distributed).
We tested for heteroskedasticity using the Breusch-Pagan test (null hypothesis: variable of interest has constant variance).
Warning: Non-normality of residuals detected (p < .001).Warning: Heteroscedasticity (non-constant error variance) detected (p < .001).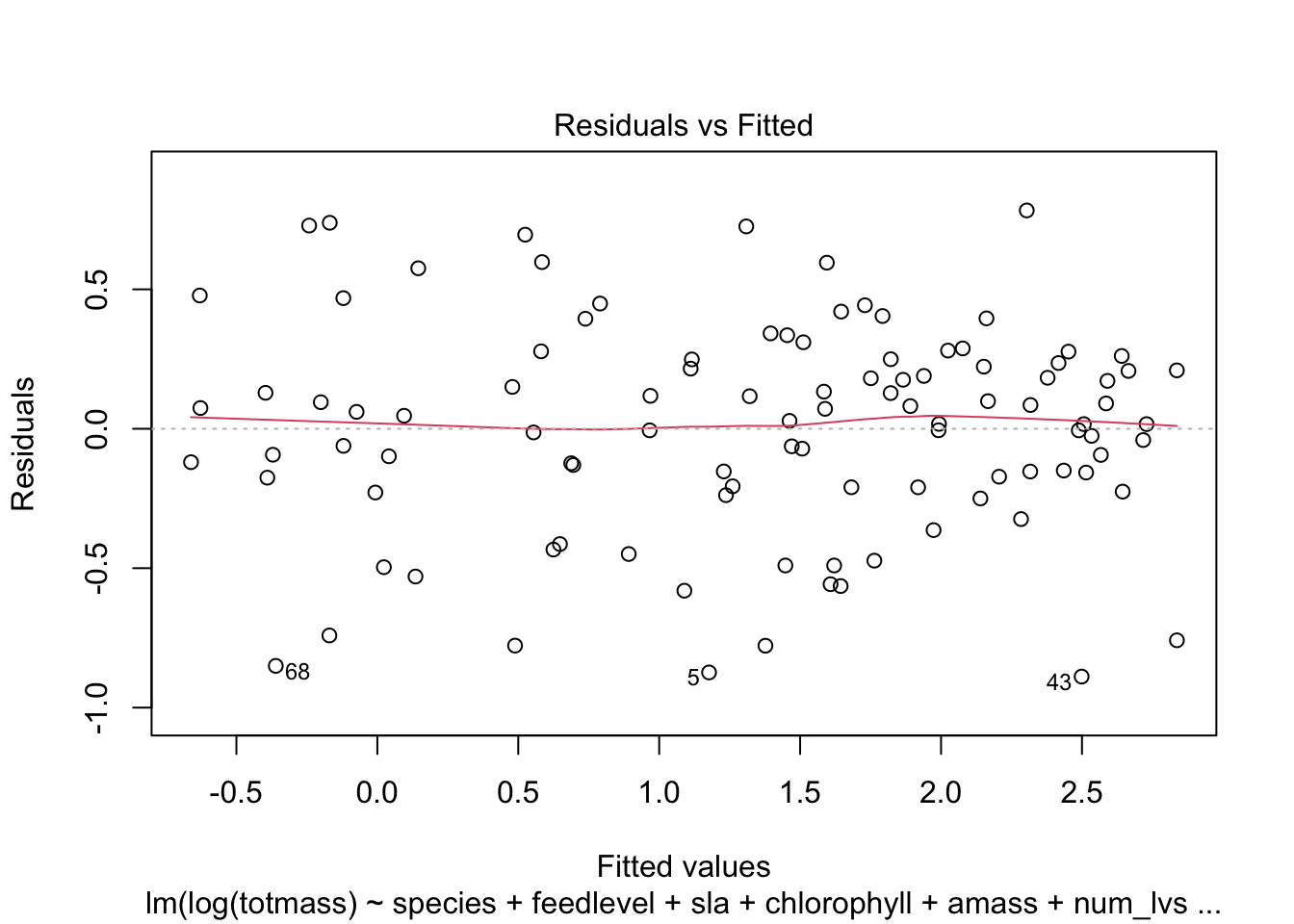
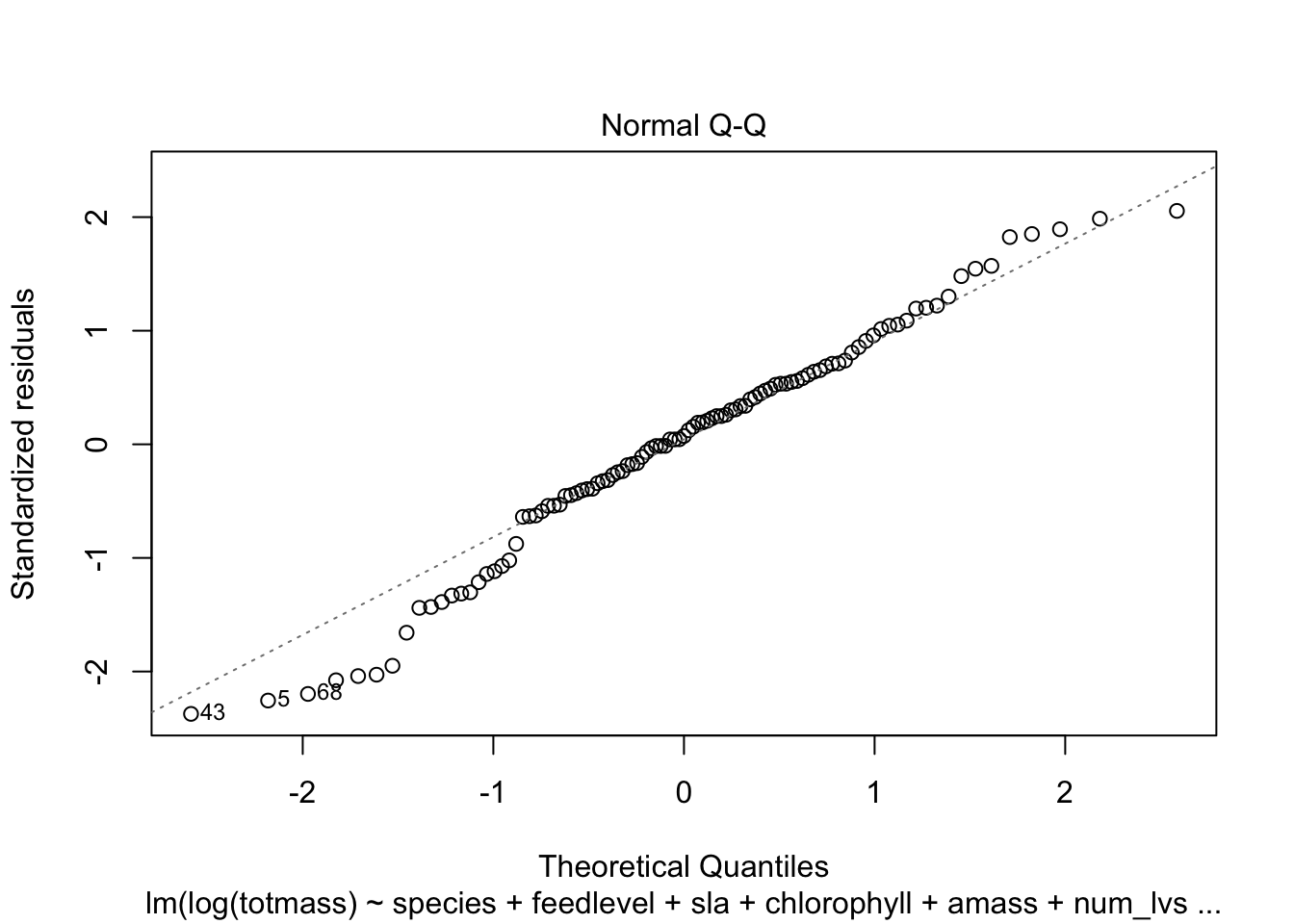
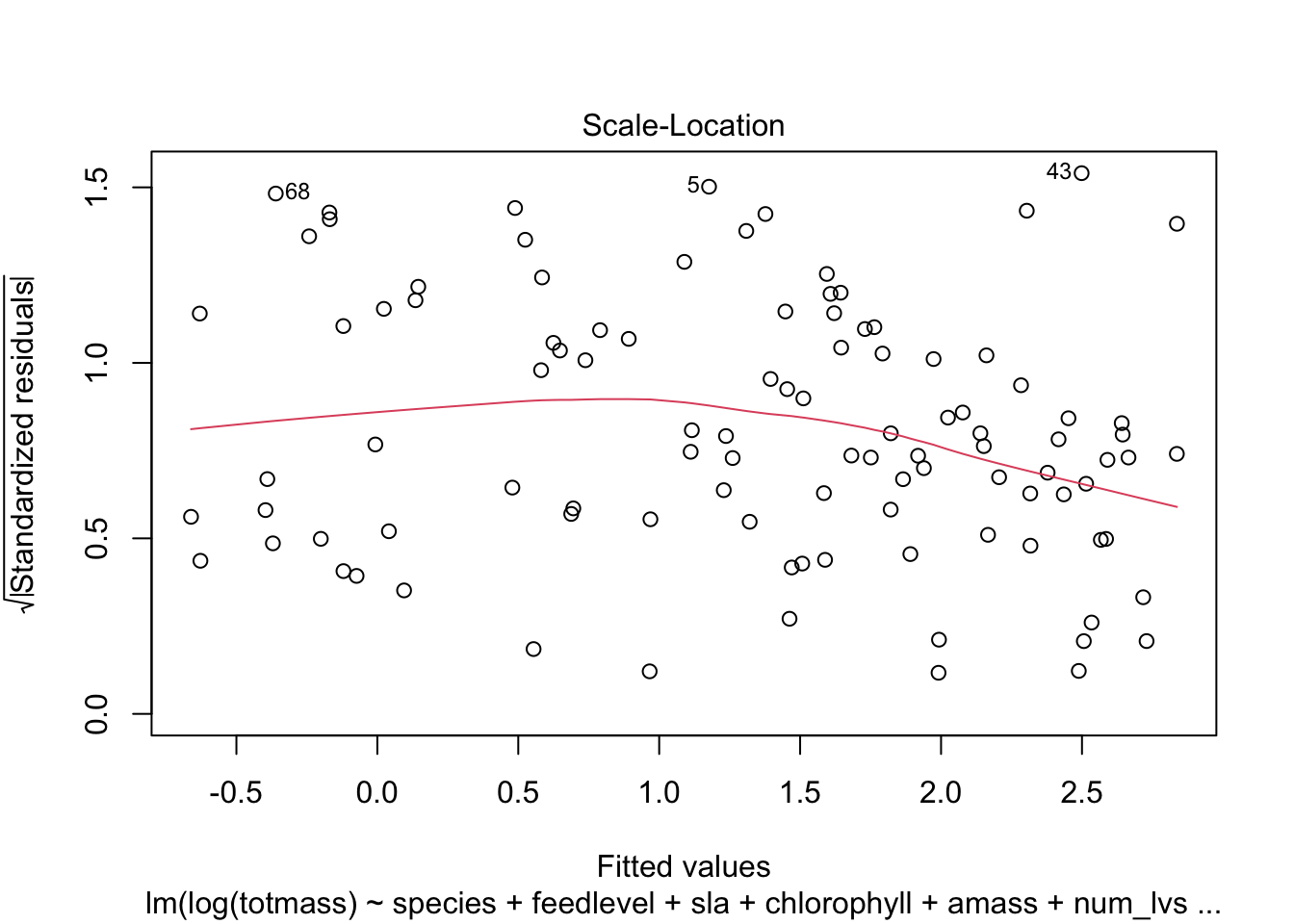
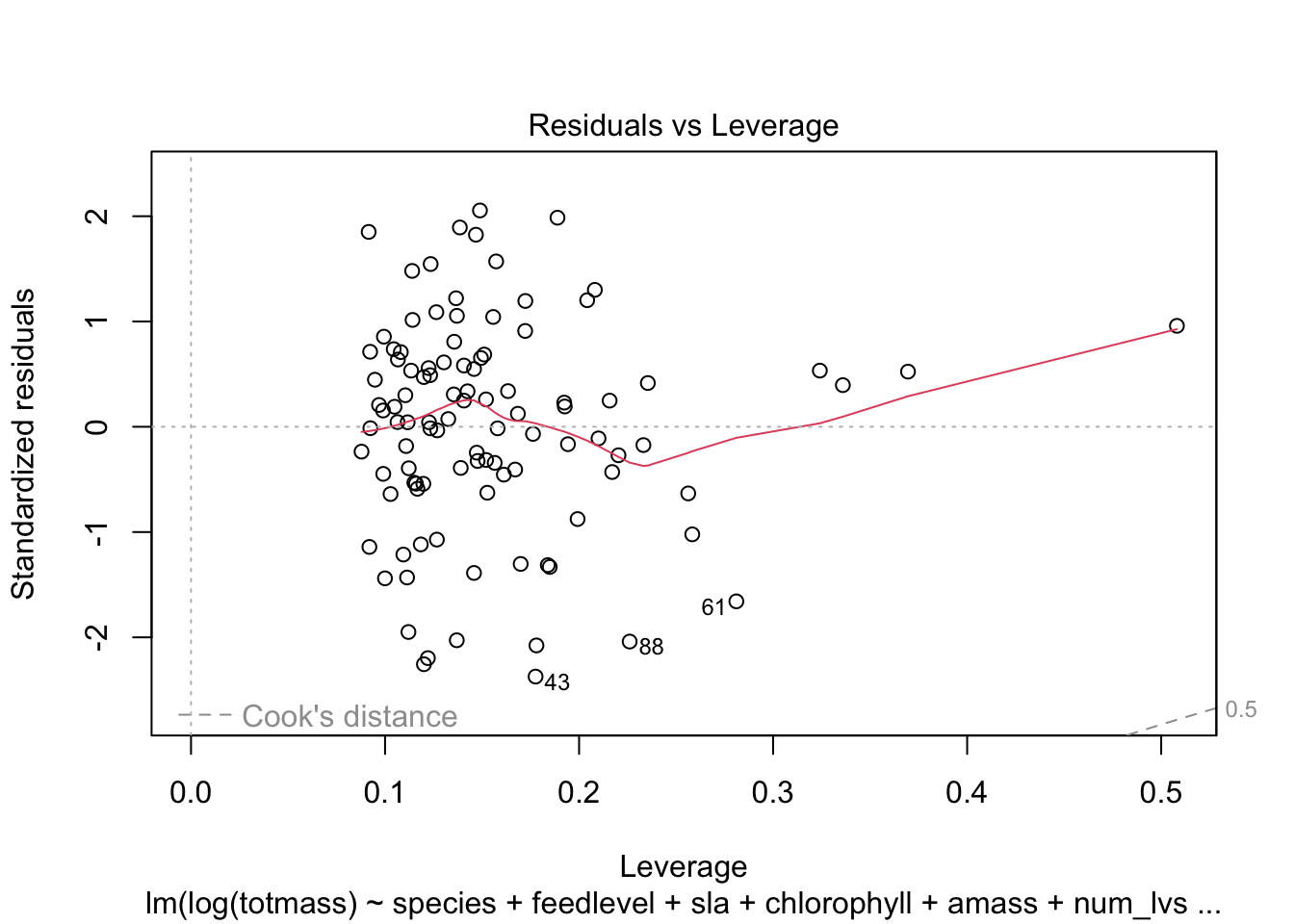
OK: residuals appear as normally distributed (p = 0.107).OK: Error variance appears to be homoscedastic (p = 0.071).Evaluate multicollinearity:
GVIF Df GVIF^(1/(2*Df))
species 42.351675 9 1.231351
feedlevel 1.621993 1 1.273575
sla 1.999989 1 1.414210
chlorophyll 1.949828 1 1.396362
amass 2.872084 1 1.694722
num_lvs 2.813855 1 1.677455
num_phylls 2.995510 1 1.730754We evaluated multicollinearity by calculating generalized variance inflation factor and determined that…
try some more models:
addressing the question: what set of predictor variables best explains the response?
check assumptions for model 2:
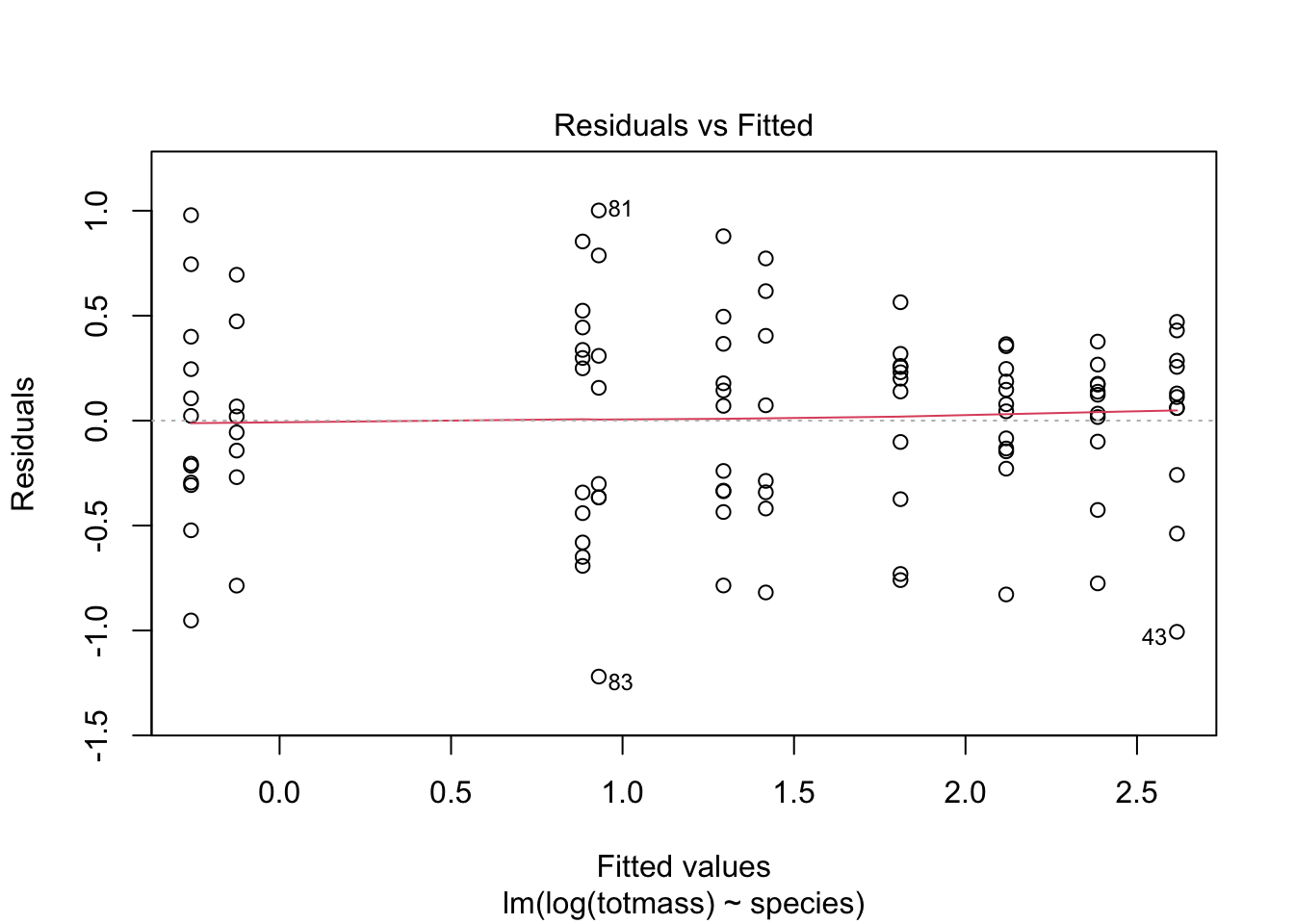
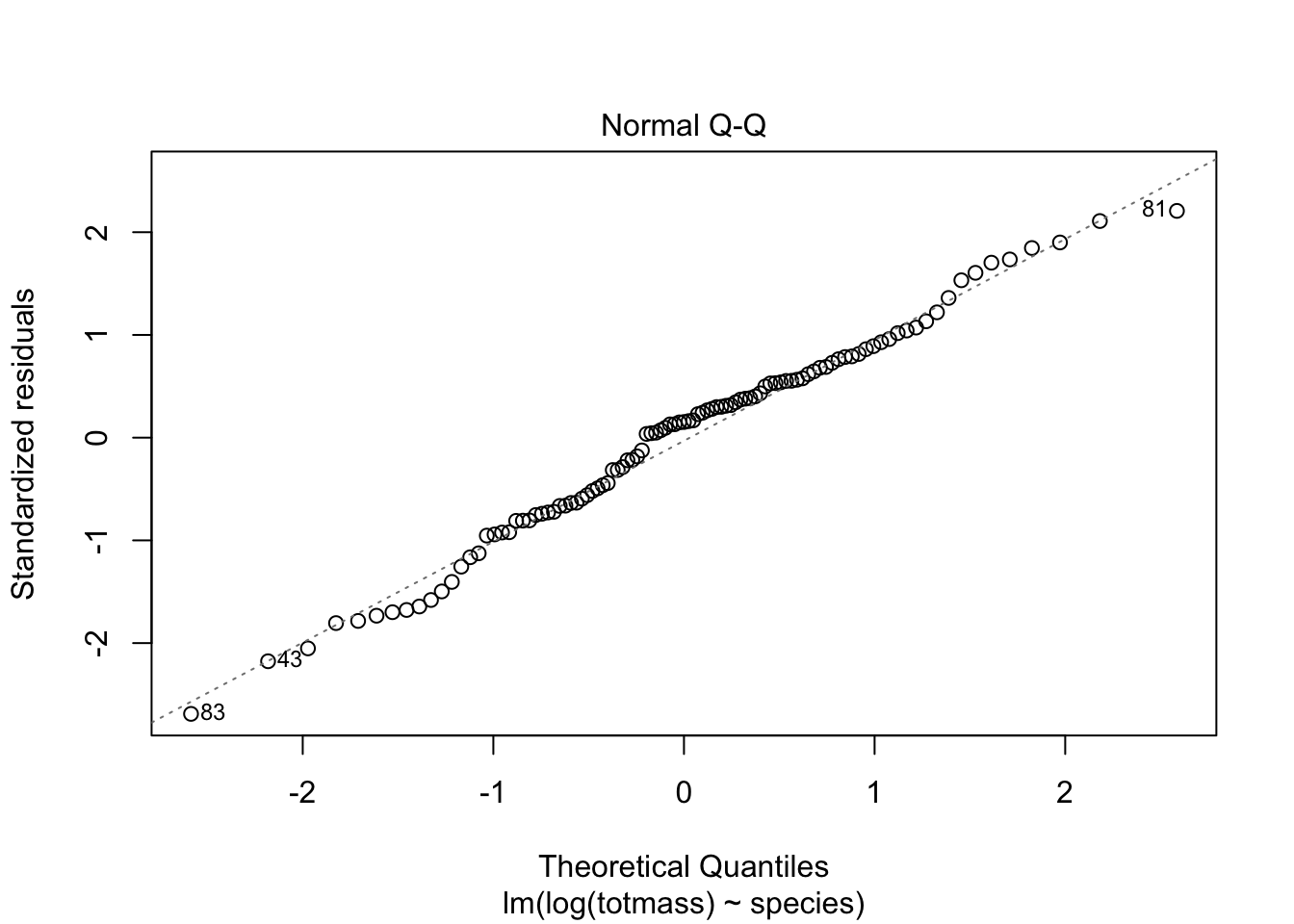
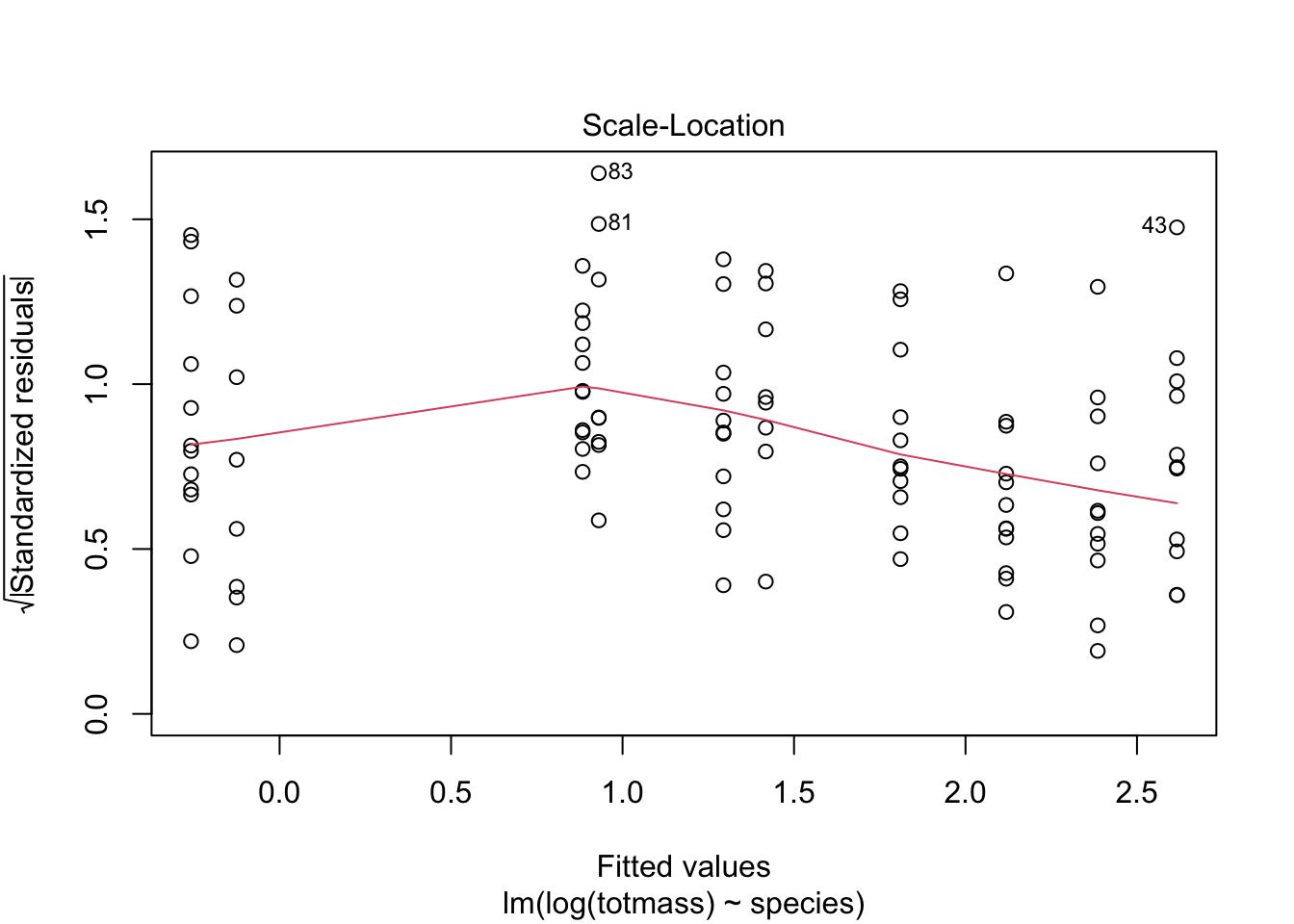
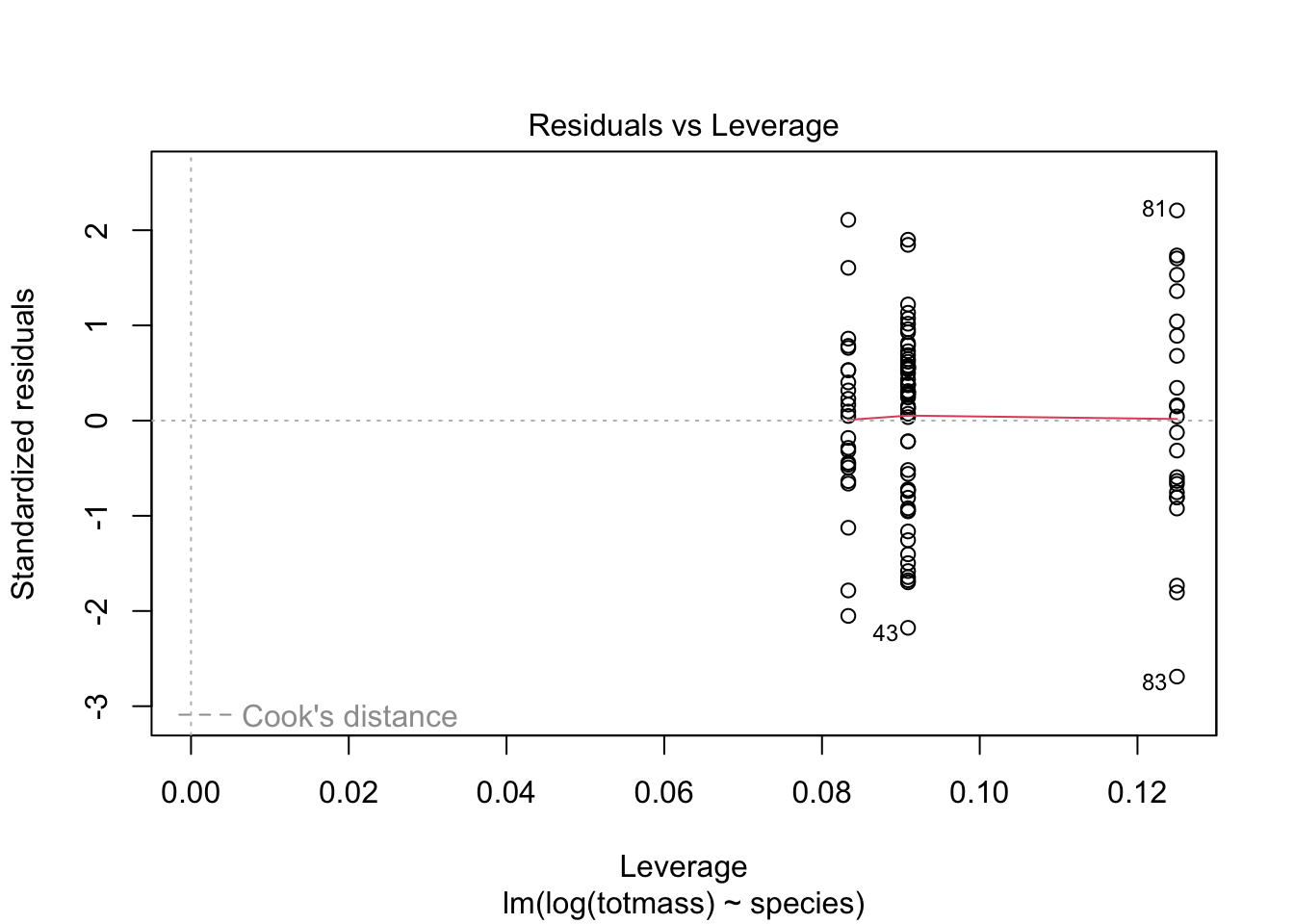
OK: residuals appear as normally distributed (p = 0.374).OK: Error variance appears to be homoscedastic (p = 0.100).compare models using Akaike’s Information criterion (AIC) values:
[1] 133.9424[1] 157.5751[1] 306.0028 df AICc
full_log 17 133.9424
model2_log 11 157.5751
null_log 2 306.0028Model selection table
(Int) ams chl fdl num_lvs num_phy sla spc df
full_log -1.3390 0.002338 0.004368 -0.4743 0.09176 -0.03959 -0.002493 + 17
model2_log 0.8836 + 11
null_log 1.3500 2
logLik AICc delta weight
full_log -46.371 133.9 0.00 1
model2_log -66.337 157.6 23.63 0
null_log -150.941 306.0 172.06 0
Models ranked by AICc(x) we compared models using AIC and chose the model with the lowest value, which was…
We found that the ______ model including ___ ____ __ predictors best predicted _______ (model summary).
Call:
lm(formula = log(totmass) ~ species + feedlevel + sla + chlorophyll +
amass + num_lvs + num_phylls, data = plant_subset)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.88872 -0.20811 0.02825 0.24218 0.78287
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -1.339043 0.597727 -2.240 0.027624 *
speciesalata 1.113163 0.184021 6.049 3.56e-08 ***
speciesflava 1.404562 0.262955 5.341 7.29e-07 ***
speciesjonesii 0.319652 0.196426 1.627 0.107281
speciesleucophylla 1.709035 0.227608 7.509 4.88e-11 ***
speciesminor 0.389310 0.187903 2.072 0.041239 *
speciespsittacina -1.645198 0.207035 -7.946 6.36e-12 ***
speciespurpurea -0.364348 0.254380 -1.432 0.155643
speciesrosea -0.947383 0.260495 -3.637 0.000467 ***
speciesrubra 0.875342 0.196361 4.458 2.46e-05 ***
feedlevel -0.474255 0.234493 -2.022 0.046199 *
sla -0.002493 0.001160 -2.149 0.034430 *
chlorophyll 0.004368 0.001189 3.672 0.000414 ***
amass 0.002338 0.002988 0.782 0.436166
num_lvs 0.091764 0.022413 4.094 9.46e-05 ***
num_phylls -0.039585 0.051714 -0.765 0.446068
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.413 on 87 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8687, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8461
F-statistic: 38.38 on 15 and 87 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16term | estimate | std.error | statistic | p.value | conf.low | conf.high |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Intercept) | -1.339043200 | 0.597726532 | -2.2402271 | 0.027624109607483092 | -2.527089405 | -0.1509969955 |
speciesalata | 1.113162580 | 0.184020930 | 6.0491086 | 0.000000035633453091 | 0.747401056 | 1.4789241035 |
speciesflava | 1.404562038 | 0.262954818 | 5.3414577 | 0.000000728606298866 | 0.881910865 | 1.9272132117 |
speciesjonesii | 0.319652351 | 0.196426010 | 1.6273423 | 0.107280978897063603 | -0.070765614 | 0.7100703152 |
speciesleucophylla | 1.709035391 | 0.227608275 | 7.5086698 | 0.000000000048774953 | 1.256639298 | 2.1614314841 |
speciesminor | 0.389310367 | 0.187903472 | 2.0718636 | 0.041239074384119417 | 0.015831871 | 0.7627888636 |
speciespsittacina | -1.645197874 | 0.207034720 | -7.9464830 | 0.000000000006356134 | -2.056701798 | -1.2336939506 |
speciespurpurea | -0.364347584 | 0.254380246 | -1.4322951 | 0.155642631385407848 | -0.869955868 | 0.1412607001 |
speciesrosea | -0.947383285 | 0.260494896 | -3.6368593 | 0.000466976667424191 | -1.465145097 | -0.4296214723 |
speciesrubra | 0.875341885 | 0.196361315 | 4.4578123 | 0.000024573993550446 | 0.485052508 | 1.2656312619 |
feedlevel | -0.474255269 | 0.234492879 | -2.0224719 | 0.046198841611705344 | -0.940335257 | -0.0081752817 |
sla | -0.002493083 | 0.001160230 | -2.1487826 | 0.034429589763780327 | -0.004799167 | -0.0001869994 |
chlorophyll | 0.004368330 | 0.001189484 | 3.6724575 | 0.000414110175835846 | 0.002004101 | 0.0067325586 |
amass | 0.002337656 | 0.002988210 | 0.7822929 | 0.436166480376765642 | -0.003601736 | 0.0082770479 |
num_lvs | 0.091763935 | 0.022413350 | 4.0941643 | 0.000094562482452723 | 0.047214976 | 0.1363128941 |
num_phylls | -0.039585071 | 0.051713890 | -0.7654630 | 0.446067519262092982 | -0.142372027 | 0.0632018848 |
use ggpredict() to backtranform estimates
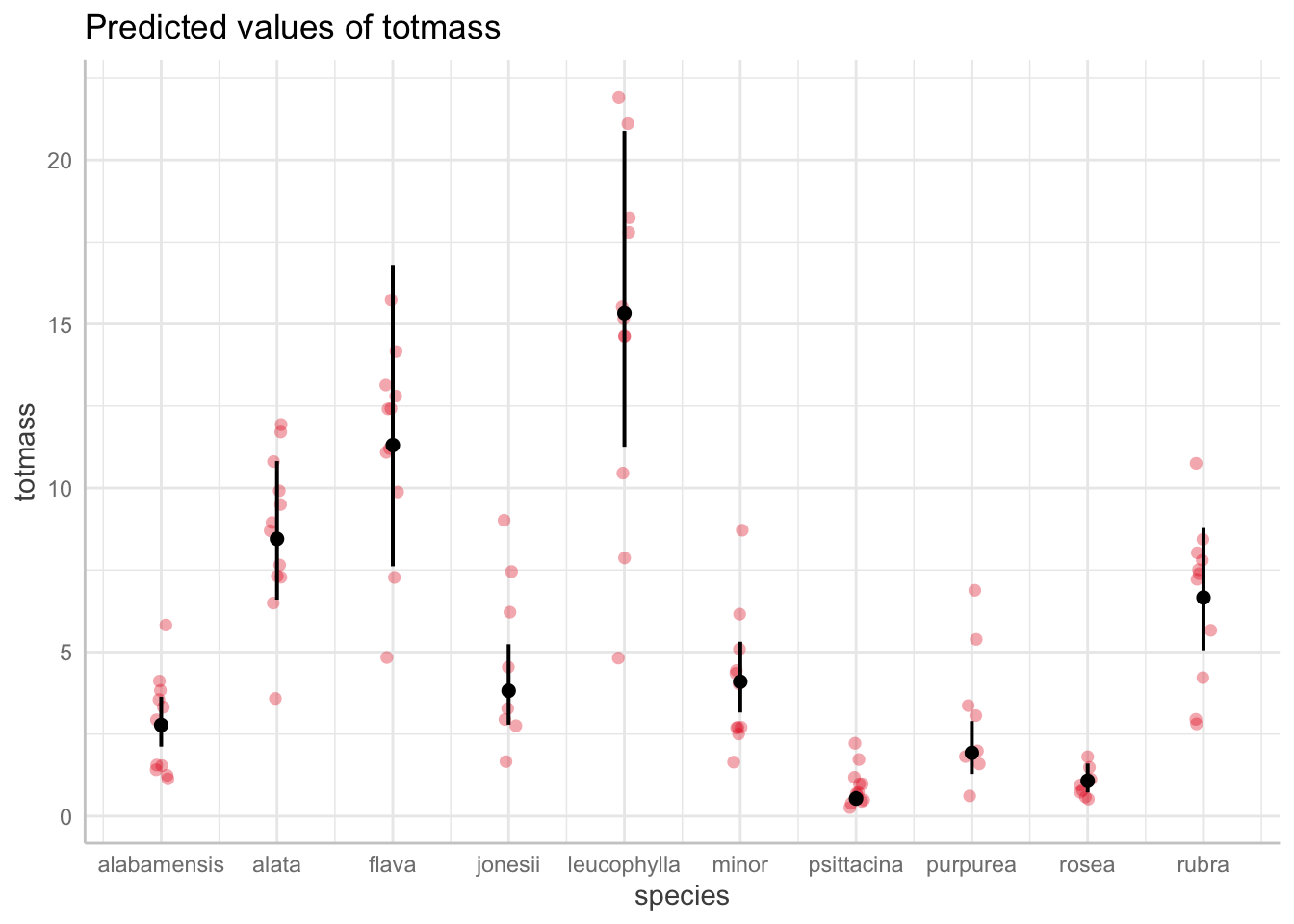
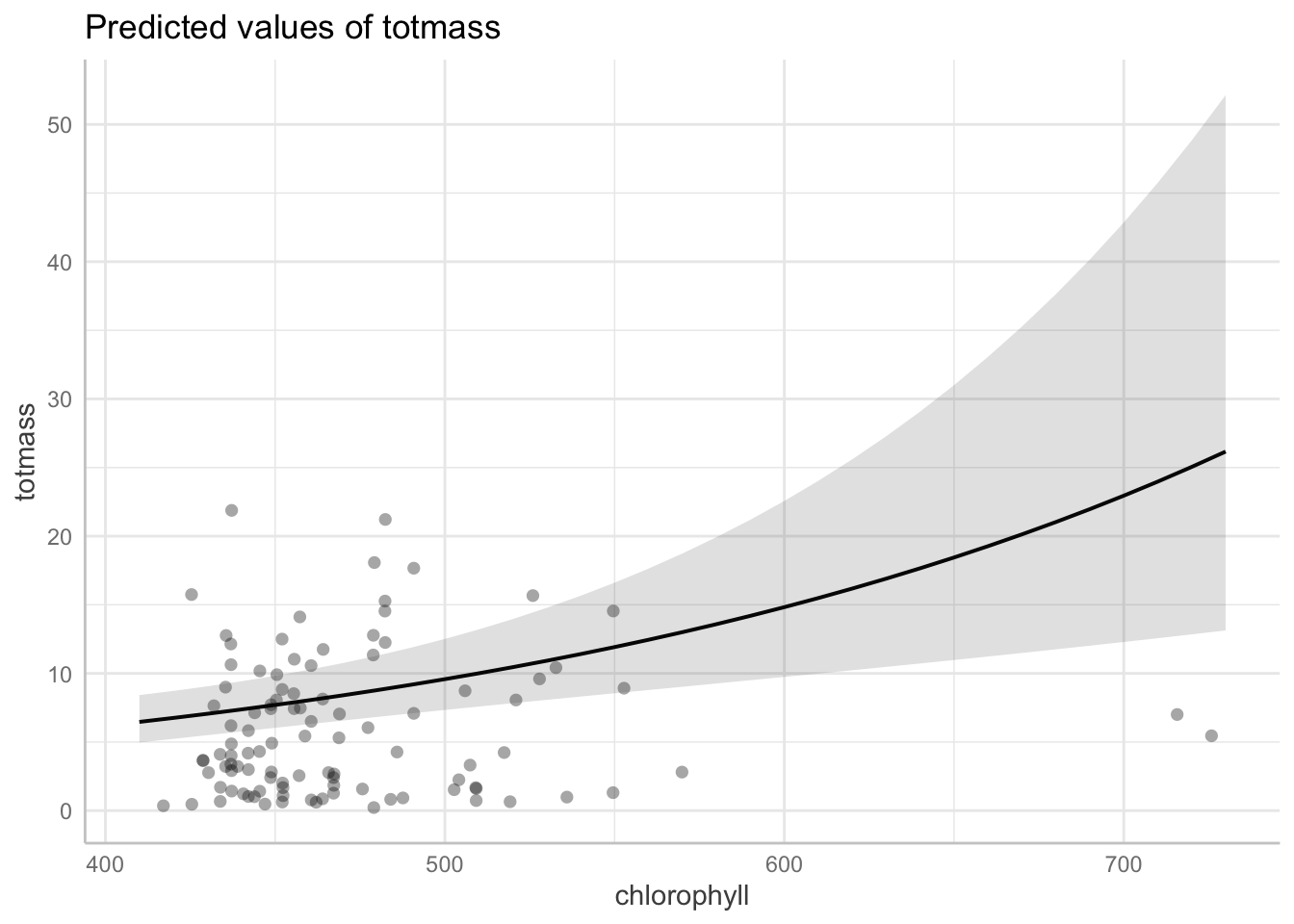
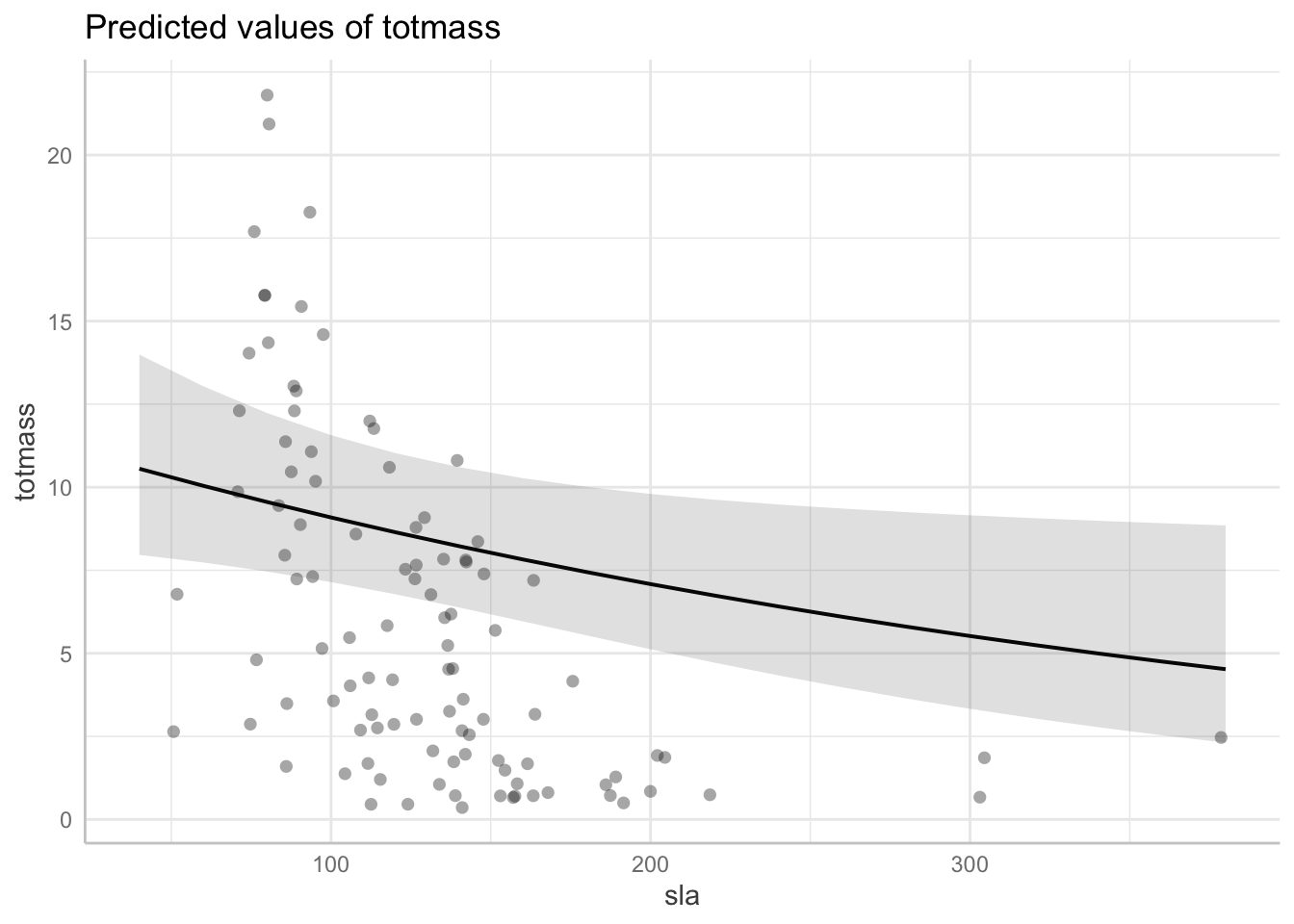
# Predicted values of totmass
species | Predicted | 95% CI
---------------------------------------
alabamensis | 2.78 | [2.12, 3.64]
alata | 8.45 | [6.60, 10.82]
flava | 11.31 | [7.61, 16.80]
jonesii | 3.82 | [2.79, 5.24]
minor | 4.10 | [3.16, 5.31]
psittacina | 0.54 | [0.37, 0.77]
purpurea | 1.93 | [1.28, 2.90]
rubra | 6.66 | [5.05, 8.78]
Adjusted for:
* feedlevel = 0.18
* sla = 129.27
* chlorophyll = 471.29
* amass = 35.26
* num_lvs = 7.08
* num_phylls = 0.58@online{bui2023,
author = {Bui, An},
title = {Coding Workshop: {Week} 8 and 9},
date = {2023-05-24},
url = {https://an-bui.github.io/ES-193DS-W23/workshop/workshop-08_2023-05-24.html},
langid = {en}
}